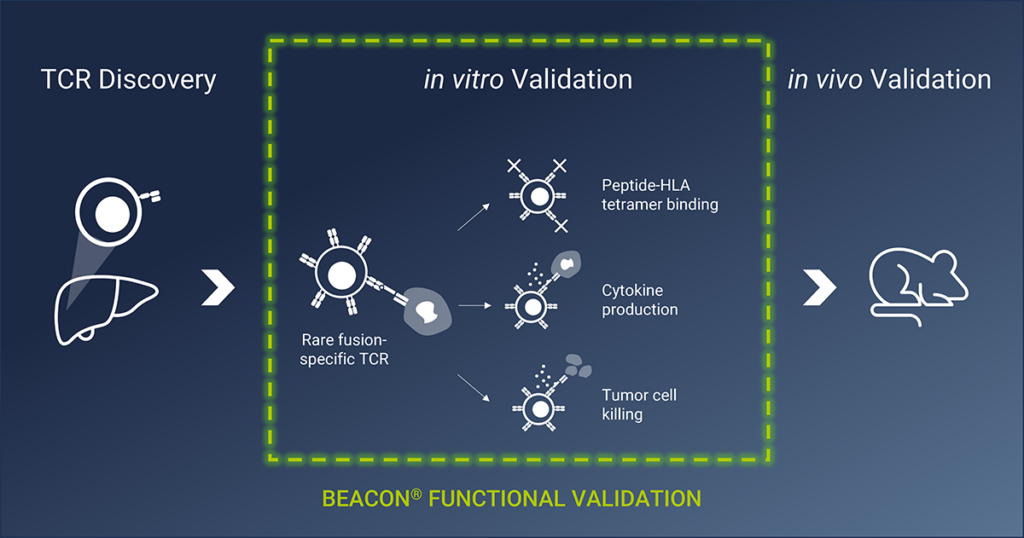
In a new publication in Cell Reports Medicine from researchers at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and the University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC), researchers used Bruker Cellular Analysis’s Beacon® Platform to validate the functional performance of engineered T cells generated to combat fibrolamellar carcinoma (FLC) by recognizing cancer-specific fusion proteins. The study used these groundbreaking findings to construct cell therapies and showed cancer killing results in a mouse model.
FLC is a rare liver cancer that is more frequently found in young adults. Affected patients lack symptoms in early stages so by the time most patients are diagnosed with the disease at advanced stages, they often face poor prognosis. 90% of FLC patients harbor an aberrant fusion mutation of the genes DNAJB1 and PRKACA resulting in uncontrolled cell division and malignancy. The fusion protein highly conserved in FLC, making it a valid candidate for a novel T cell based therapy . Unfortunately, there are many challenges in identifying the T cells that can recognize these cancer-specific mutations since the occurrence is extremely rare. Even though the fusion mutation was identified 10 years ago, the quest for finding the T cells that may recognize the fusion protein has been unsuccessful until now.
The St. Jude-UTHSC team successfully discovered two TCRs capable of attacking cancer cells expressing the mutated protein but needed further proof of functionality to proceed towards in vivo experiments. They successfully utilized the Beacon platform to perform high-throughput real-time monitoring and screening of thousands of engineered T cells to validate functionality at a single-cell level. The Beacon allowed them to assess cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion which revealed that one of their candidates was capable of greater levels of cytotoxicity and polyfunctional cytokine secretion Furthermore, they were able to progress toward using this candidate in in vivo mouse models, laying a strong foundation of a promising cell therapy for treating patients.